Course Title: Engine Technology
Course Description:
The Engine Technology course is a comprehensive program designed to equip learners with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary to understand, maintain, diagnose, and repair internal combustion engines and related systems. This course provides an in-depth study of both gasoline (petrol) and diesel engines, covering their construction, operation, components, performance characteristics, and emissions control.
Through a blend of classroom instruction, laboratory sessions, and hands-on practical experience, students will learn the functioning of various engine systems, including fuel systems, ignition systems, lubrication, cooling, intake and exhaust systems. Emphasis is also placed on engine diagnostics, fault detection, service procedures, and adherence to safety and environmental standards.
The course aligns with current industry practices and introduces learners to modern engine technologies such as electronic fuel injection (EFI), turbocharging, engine control units (ECUs), hybrid systems, and alternative fuel engines.
Course Objectives:
By the end of the course, students should be able to:
Understand the principles of internal combustion engines (ICE).
Identify and describe engine components and their functions.
Perform routine engine maintenance and repairs.
Use diagnostic tools and procedures to troubleshoot engine faults.
Understand and apply safety standards and environmental regulations.
Explain the operation of advanced engine systems such as EFI and turbochargers.
Interpret technical manuals and service documentation.
Key Topics Covered:
1. Introduction to Engine Technology
History and evolution of engines
Types of engines (2-stroke, 4-stroke, petrol, diesel, hybrid)
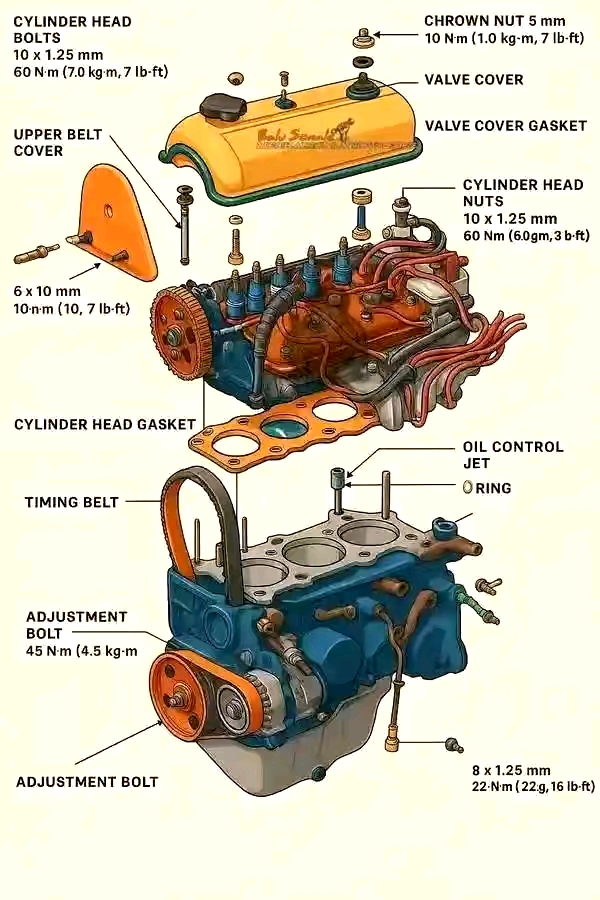
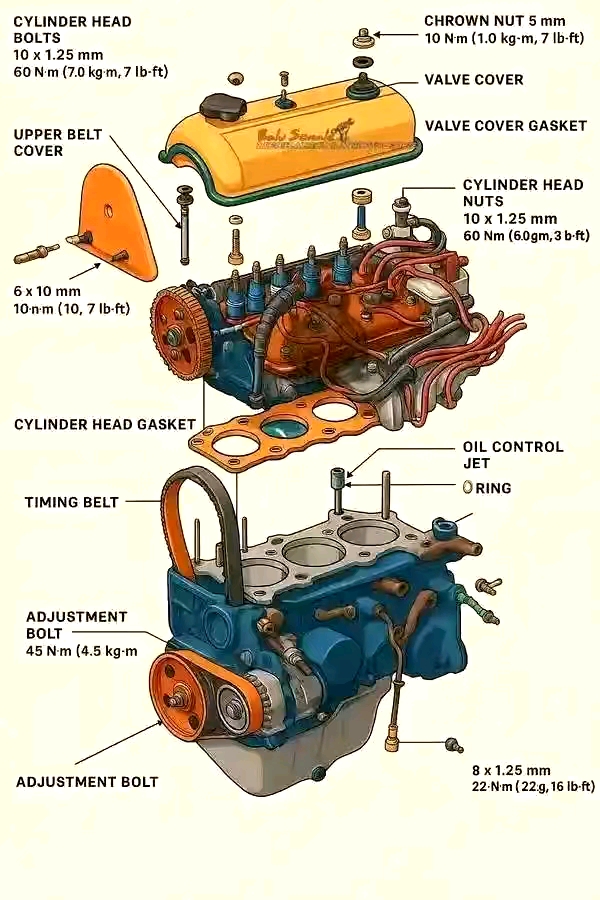
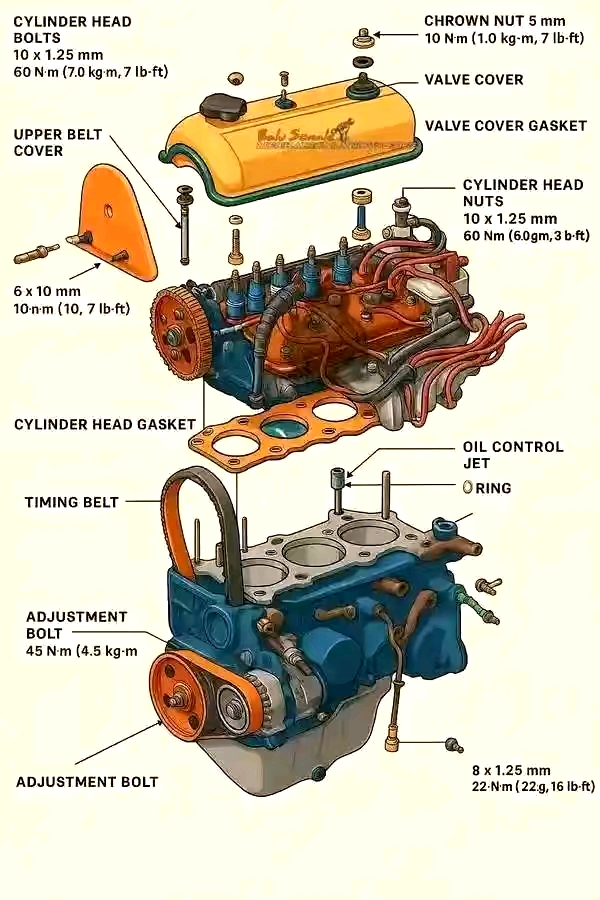
2. Engine Design and Components
Engine block, crankshaft, piston, camshaft, valves, etc.
Cylinder arrangements and firing order
3. Working Principles of Engines
Otto and Diesel cycles
2-stroke vs. 4-stroke operation
4. Fuel Systems
Carburetors
Fuel injection systems (Mechanical and Electronic)
Diesel injection systems
5. Ignition Systems
Contact breaker point systems
Electronic ignition systems
6. Lubrication and Cooling Systems
Oil types and lubrication circuits
Air and liquid cooling systems
7. Intake, Exhaust, and Emissions
Air-fuel ratio, intake manifolds
Exhaust systems and catalytic converters
Emission control regulations
8. Engine Performance and Efficiency
Engine tuning
Power and torque measurements
9. Engine Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Use of diagnostic tools (OBD scanners, compression testers)
Common faults and repair procedures
10. Advanced Engine Technologies
Turbochargers and superchargers
Variable valve timing (VVT)
Hybrid engines and alternative fuels (LPG, CNG, EV basics)
11. Workshop Practice and Safety
Workshop safety rules
Proper tool usage
Environmental considerations
Target Group:
Automotive engineering students
Motor vehicle technicians
TVET learners in mechanical or automotive trades
Anyone interested in engine repair and technology
Course Duration:
Typically 1–2 academic years, depending on level (Artisan, Craft, Diploma)
Assessment Methods:
Written examinations
Practical assessments
Assignments and projects
Industria
l attachment/internship reports